Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB refers to sintered neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnets manufactured in a trapezoidal geometry to meet specific magnetic circuit and mechanical assembly requirements. Products within this category share common characteristics such as high magnetic energy density, precise angular geometry, and suitability for structured magnetic systems where linear or curved flux distribution is required. Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB magnets are widely used in rotating equipment, segmented magnetic assemblies, and electromagnetic conversion systems where shape accuracy directly affects performance and efficiency.
Common Functions and Core Performance Characteristics
All Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB products are based on sintered NdFeB material, which provides high remanence (Br), coercivity (Hcj), and maximum energy product (BHmax). The trapezoidal shape enables optimized magnetic field alignment, reduced air gaps, and improved flux concentration in complex assemblies.
Key shared characteristics include:
-
Stable magnetic output under compact design constraints
-
Compatibility with segmented rotor and stator structures
-
High dimensional accuracy to support repeatable magnetic performance
-
Suitability for medium- to high-speed electromagnetic equipment
These properties make Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB a standard choice in systems where magnetic efficiency and structural fit must be balanced.
Working Principles by Equipment Type
Electric Motors and Generators
In permanent magnet motors, trapezoidal magnets are arranged circumferentially on the rotor. The trapezoidal geometry allows tighter fitting between adjacent magnets, reducing flux leakage and improving torque density. The sintered NdFeB material provides a stable magnetic field that interacts with stator windings to generate rotational force or electrical output.
Magnetic Couplings and Transmission Devices
In magnetic couplings, Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB magnets are positioned to create alternating magnetic poles. Torque is transmitted through magnetic interaction rather than mechanical contact, enabling sealed transmission systems and reduced wear.
Sensor and Actuator Systems
The controlled magnetic field distribution of trapezoidal magnets supports precise position detection and force control. Their predictable magnetic behavior improves signal stability in industrial sensors and linear actuators.
Typical Application Scenarios
-
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM)
-
Wind power generators and auxiliary drive systems
-
Industrial automation equipment
-
Magnetic pumps and sealed transmission systems
-
Automotive electric drive components
In many of these applications, manufacturers select Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB to match curved housings or segmented magnetic paths, ensuring consistent magnetic flux across the working area.
Comparison with Other NdFeB Shapes
| Aspect | Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB | Arc / Segment NdFeB | Block NdFeB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Circuit Fit | Optimized for angled or circular assemblies | Optimized for circular rotors | General-purpose |
| Flux Utilization | High | High | Moderate |
| Assembly Precision | High | High | Lower |
| Typical Use | Motors, generators | High-end motors | Fixtures, holding systems |
Compared with standard block magnets, Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB provides improved magnetic field continuity in rotational systems. Compared with arc-shaped magnets, trapezoidal designs allow greater flexibility in segmented assemblies and tooling control.
Surface Treatment and Environmental Adaptation
Most products in this category use protective coatings such as nickel, epoxy, or zinc to reduce corrosion risks. Selection depends on operating temperature, humidity, and exposure conditions. For industrial environments with oil or moisture exposure, epoxy-coated trapezoid magnets are commonly specified.
Maintenance and Handling Guidelines
Although sintered NdFeB magnets are permanent and require no active maintenance, proper handling and system-level maintenance help ensure long-term performance:
-
Avoid mechanical impact during installation to prevent chipping
-
Maintain operating temperatures within the specified grade limits
-
Prevent direct contact with corrosive substances if coating is damaged
-
Inspect magnet positioning during scheduled equipment maintenance
Correct installation alignment is especially important for Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB, as angular deviation can affect magnetic balance in rotating systems.
Manufacturing and Quality Control Considerations
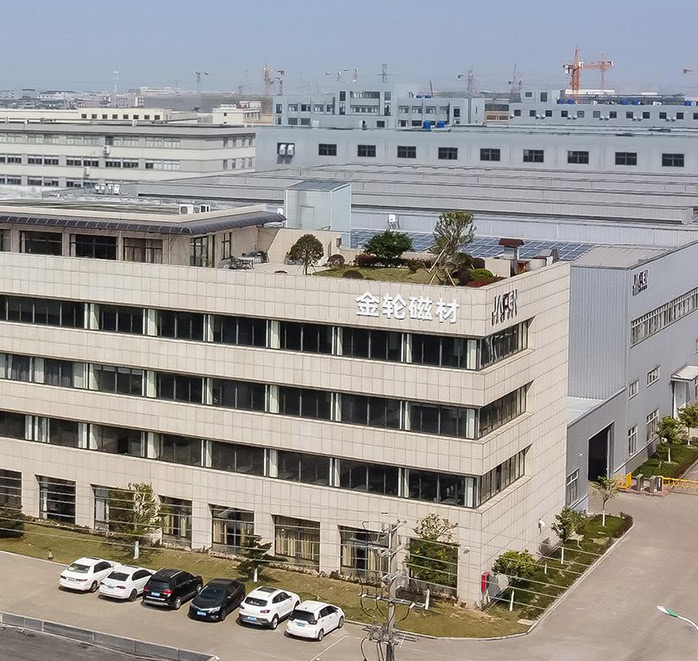
Ningbo Jinlun Magnet Technology Co., Ltd. produces Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB using controlled powder metallurgy processes, including orientation pressing, vacuum sintering, and precision machining. With over 30 years of industry experience and an annual capacity of 8,000 tons of high-performance magnets, Jinlun Magnet supports stable material properties and consistent dimensional accuracy for industrial applications.
The company’s production process emphasizes:
-
Controlled grain orientation for predictable magnetic output
-
Dimensional tolerance control for segmented assemblies
-
Grade customization based on temperature and coercivity requirements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why choose trapezoidal magnets instead of rectangular ones?
Trapezoidal magnets improve magnetic circuit continuity in curved or segmented assemblies, reducing flux loss compared to rectangular shapes.
Q2: Are Trapezoid Sintered NdFeB magnets suitable for high-speed motors?
Yes. When correctly specified for coercivity and temperature resistance, they are commonly used in high-speed rotating equipment.
Q3: Can the magnet grade be customized for different operating temperatures?
Yes. Different NdFeB grades can be selected to match operating temperature ranges and demagnetization resistance.
Q4: What tolerances are typical for trapezoidal magnets?
Tolerances depend on size and application, but precision machining allows consistent angular and dimensional control suitable for motor assemblies.
 EN
EN English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Deutsch
Deutsch 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어